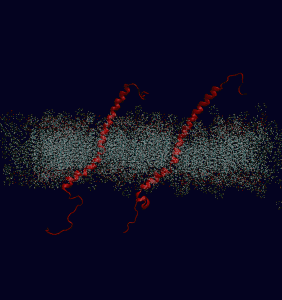
 Through these computer simulations at Berkeley, it creates a virtual structure of integrin twenty nanometers long. In this simulation, the integrin responds to stimuli the way actual integrin do. Now, reserachers will be able to discover how an integrin connects to the internal and external environments of a cell.
Through these computer simulations at Berkeley, it creates a virtual structure of integrin twenty nanometers long. In this simulation, the integrin responds to stimuli the way actual integrin do. Now, reserachers will be able to discover how an integrin connects to the internal and external environments of a cell.Results that have already been found report that "when activated by an external force, integrins cluster together on a cell's surface and join other proteins to form structures called focal adhesions". Researchers have concluded that the ability to cluster together is because a subunit of an integrin is connected to actin filaments, a protein which forms the skeleton of a cell.
The hunt continues as scientists use this new breakthrough to discover more about integrin.
NOS Themes:
Science is collaborative; multiple scientists of UC Berkeley worked together to create a computer simluation of an integrin, and combined their efforts to draw conclusions.
Role of Credibility; it can be assumed that this computer simulation is accurate since Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been acknowledged by the awards of 13 Nobel prizes.
The role of motivation and curiosity; scientists of UC Berkeley wanted to figure out why integrins react around each other the way they do in order to explain how cells interact with each other.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/03/130322174339.htm
Adrianna Tan Hour 3
No comments:
Post a Comment